Welcome to the weekly digest about the Cybersecurity & Threats in the wild.
Below you will find a very subjective summary of Cybersecurity events for the prior week.
1.CVE-2025-8671 – HTTP/2 MadeYouReset Vulnerability DDoS Attack by @CyfirmaR
- CVE-2025-8671 (“MadeYouReset“) – newly disclosed HTTP/2 denial-of-service (DoS) vuln identified by researchers at Tel Aviv University & Imperva
- exploits weakness in some HTTP/2 implementations that incorrectly treat server-sent stream resets as stream closures
- attackers can trigger servers to reset streams using crafted HTTP/2 frames, while backend processing continues-thus bypassing standard MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS limit & exhausting server resources
https://www.cyfirma.com/research/cve-2025-8671-http-2-madeyoureset-vulnerability-ddos-attack/
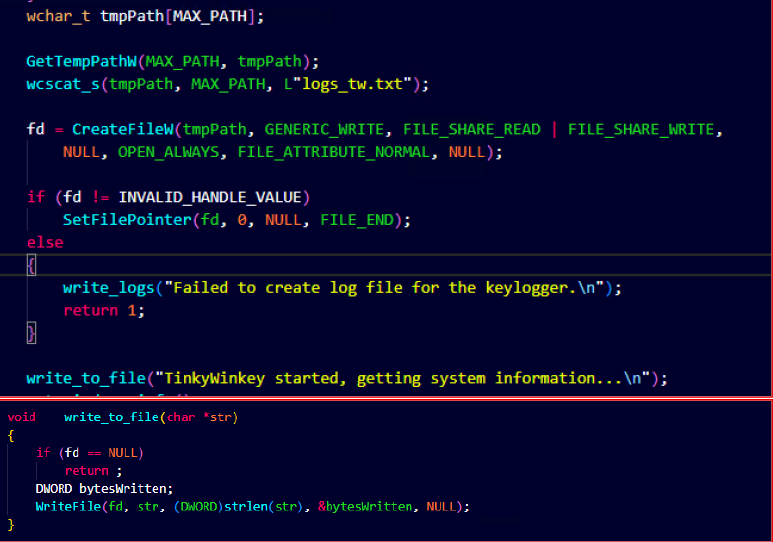
2.TINKYWINKEY KEYLOGGER by @CyfirmaR
- comprehensive analysis of TinkyWinkey Keylogger, highlighting its use of advanced Windows system programming techniques, such as service management, low-level keyboard hooks, process handling, and system info collection
- operates stealthily as service and executable, capturing extensive system data including CPU specifications, memory, OS version, and network details, while continuously monitoring active windows & keyboard layouts
https://www.cyfirma.com/research/tinkywinkey-keylogger/
3.UNVEILING A PYTHON STEALER – INF0S3C STEALER by @CyfirmaR
- Python-based grabber designed to collect system info & user data
- executable imports range of Windows APIs for file & directory operations, process enumeration, system configuration access, memory manipulation, and security management, supporting its data collection & operational functionality
https://www.cyfirma.com/research/unveiling-a-python-stealer-inf0s3c-stealer/
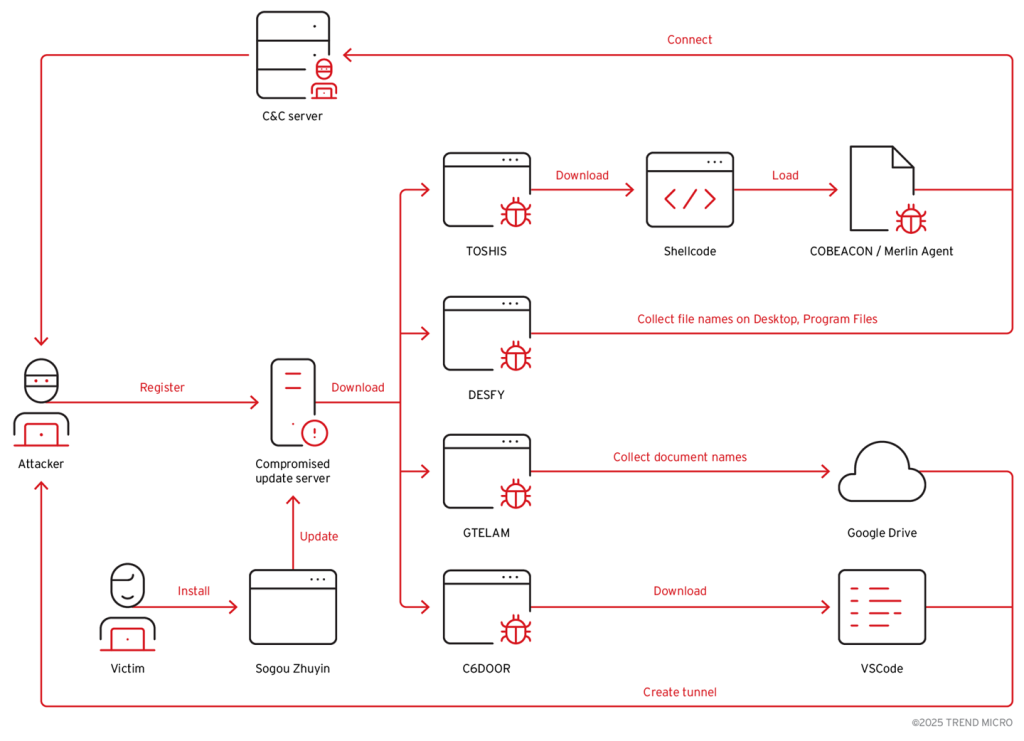
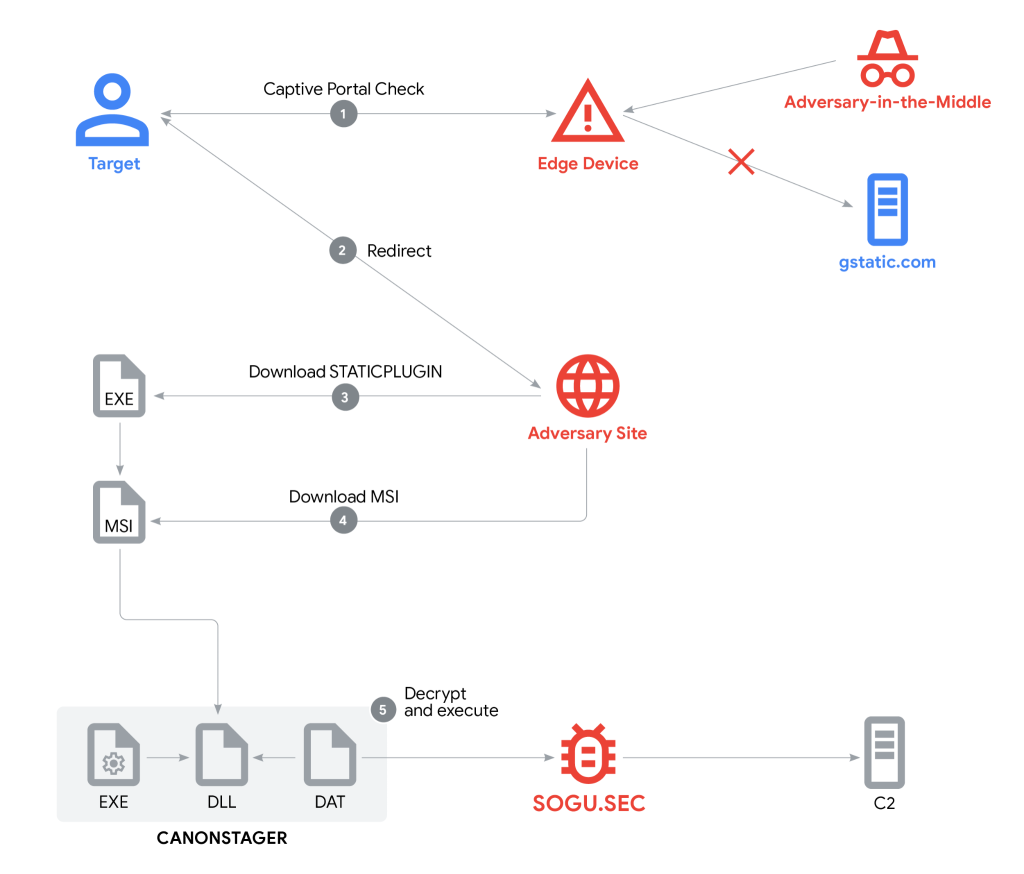
4. TAOTH Campaign Exploits End-of-Support Software to Target Traditional Chinese Users and Dissidents by @TrendMicro
- campaign leveraged abandoned Sogou Zhuyin IME update server & spear-phishing operations to deliver multiple malware families—including TOSHIS, C6DOOR, DESFY, and GTELAM—primarily targeting users across Eastern Asia
- attackers employed sophisticated infection chains, such as hijacked software updates and fake cloud storage or login pages, to distribute malware & collect sensitive info
https://www.trendmicro.com/en_us/research/25/h/taoth-campaign.html
5.First known AI-powered ransomware uncovered by ESET Research by @ESETresearch
- malware, which ESET has named PromptLock, has the ability to exfiltrate, encrypt and possibly even destroy data, though this last functionality appears not to have been implemented in the malware yet
6.Deception in Depth: PRC-Nexus Espionage Campaign Hijacks Web Traffic to Target Diplomats by @Mandiant
- complex, multifaceted campaign attributed to the PRC-nexus threat actor UNC6384
- campaign targeted diplomats in Southeast Asia and other entities globally likely in support of cyber espionage ops aligned with strategic interests of People’s Republic of China (PRC).
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/prc-nexus-espionage-targets-diplomats
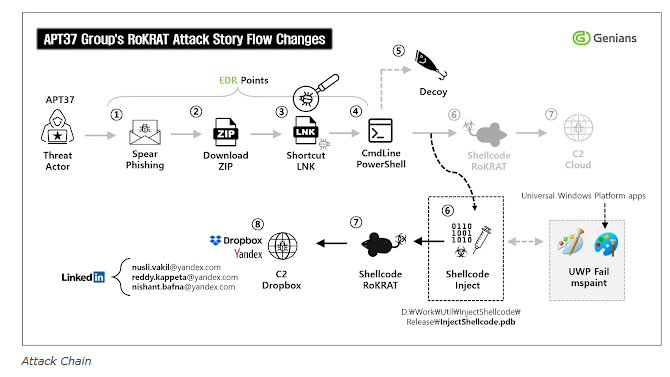
7.Stopping APT37 Before the First Click by @menlosecurity
- threat actors like APT37 continue to innovate — hiding malware in images, documents, and web content — traditional detection-based tools fall short
https://www.menlosecurity.com/blog/stopping-apt37-before-the-first-click
8. Loophole allows threat actors to claim VS Code extension names by @ReversingLabs
- discovery of loophole on VS Code platform that allowed for reuse of legitimate, but discontinued VS Code extension names by malicious actors
https://www.reversinglabs.com/blog/malware-vs-code-extension-names
9.Threat Actors Deploy Sinobi Ransomware via Compromised SonicWall SSL VPN Credentials by @esthreat
- ransomware attack attributed to affiliate of Sinobi Group
- fue to significant code overlaps and other similarities in ransomware binaries and data leak sites, Sinobi is suspected to be rebrand of Lynx, Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) group that first emerged in 2024
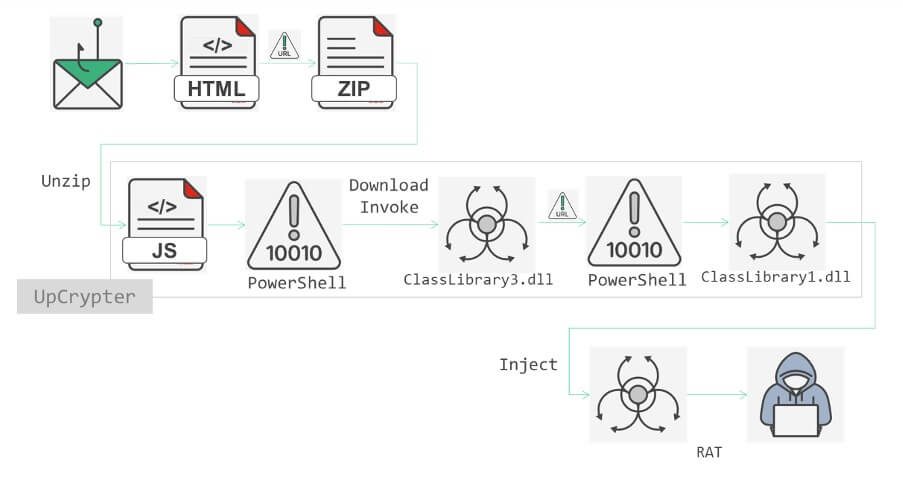
10.Phishing Campaign Targeting Companies via UpCrypter by #FORTIGUARD LABS
- phishing campaign leveraging carefully crafted emails to deliver malicious URLs linked to convincing phishing pages
- pages are designed to entice recipients into downloading JavaScript files that act as droppers for UpCrypter, malware that ultimately deploys various RATs
https://www.fortinet.com/blog/threat-research/phishing-campaign-targeting-companies-via-upcrypter
11.The ClickFix Attack That Wasn’t: From a Fake AnyDesk Installer to MetaStealer by @HuntressLabs
- early indicators of attack look like another ClickFix scam – little bit of digging shows unique infection chain that involves fake Cloudflare Turnstile lure, the Windows search protocol, and MSI package disguised as a PDF that cleverly grabs the victim’s hostname
- attack ultimately aims to drop MetaStealer, known for harvesting credentials and stealing files
https://www.huntress.com/blog/fake-anydesk-clickfix-metastealer-malware
12.How Prompt Injection Exposes Manus’ VS Code Server to the Internet by @wunderwuzzi23
- end-to-end indirect prompt injection attack leading to a compromise of Manus’ dev box
13. AWS Kiro: Arbitrary Code Execution via Indirect Prompt Injection by @wunderwuzzi23
- AWS Kiro was vulnerable to arbitrary command execution via indirect prompt injection
- this means that remote attacker, who controls data that Kiro processes, could hijack it to run arbitrary operating system commands or write and run custom code
14.Cline: Vulnerable To Data Exfiltration And How To Protect Your Data by @wunderwuzzi2
- Cline is vulnerable to data exfiltration through rendering of markdown images from untrusted domains in chat box
https://embracethered.com/blog/posts/2025/cline-vulnerable-to-data-exfiltration/
15.Windsurf MCP Integration: Missing Security Controls Put Users at Risk by @wunderwuzzi23
- when adding MCP server there are often a lot of tools the server exposes
- probably the best default option is to show list to user and let them configure which ones should run automatically, which are entirely disabled, and which ones should be suggestions
16.AgentHopper: An AI Virus by @wunderwuzzi23
- idea was to have one prompt injection payload that would operate across agents & exploit them accordingly
- this was to demonstrate that conditional prompt injection can be leveraged as powerful mechanism to target specific agents
https://embracethered.com/blog/posts/2025/agenthopper-a-poc-ai-virus/
Thanks a lot for reading.
Please add interesting items you came across during the week in the comments below.