Welcome to the weekly digest about the Cybersecurity & Threats in the wild.
Below you will find a very subjective summary of Cybersecurity events for the prior week.
1.CVE-2025-0411: Ukrainian Organizations Targeted in Zero-Day Campaign and Homoglyph Attacks by @TrendMicro
- allows bypassing of Windows Mark-of-the-Web protections by double archiving files and preventing necessary security checks and allowing execution of malicious content
- vuln was actively exploited by Russian cybercrime groups via spear-phishing campaigns, using homoglyph attacks to spoof doc extensions & trick users and Windows OS into executing malicious files
- it was likely exploited as cyberespionage campaign against Ukrainian gov and civilian orgs as part of ongoing Russo-Ukraine war
https://www.trendmicro.com/en_us/research/25/a/cve-2025-0411-ukrainian-organizations-targeted.html
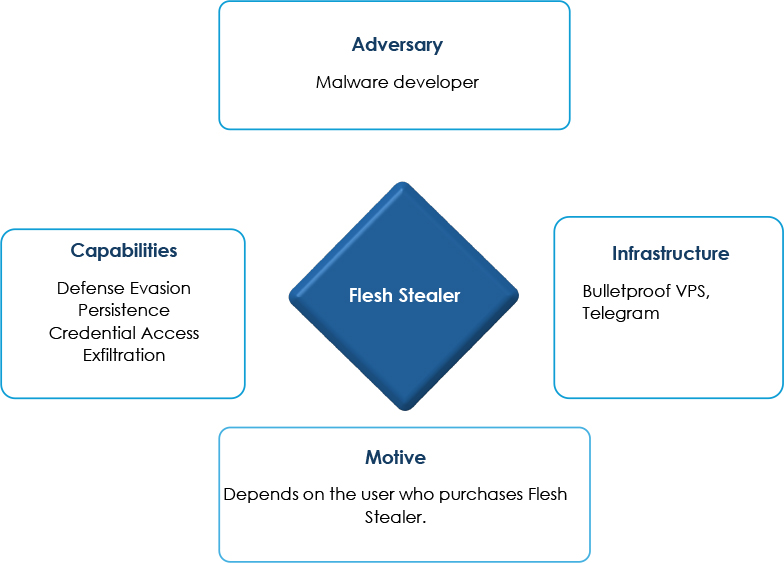
2. FLESH STEALER : UNMASKING THE BLUE MASKED THIEF by @CyfirmaR
- .NET executable written in C#
- malware does not target CIS countries
- capable of bypassing app-bound encryption employed by Chrome
- developed by Russian-speaking individual
https://www.cyfirma.com/research/flesh-stealer-unmasking-the-blue-masked-thief/
3. CVE-2023-6080: A Case Study on Third-Party Installer Abuse by @Mandiant
- exploited flaws in the Microsoft Software Installer (MSI) repair action of Lakeside Software’s SysTrack installer to obtain arbitrary code execution
- attacker with low-privilege access to a system running the vulnerable version of SysTrack could escalate privileges locally
- issue has been addressed in version 11.0.
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/cve-2023-6080-third-party-installer-abuse
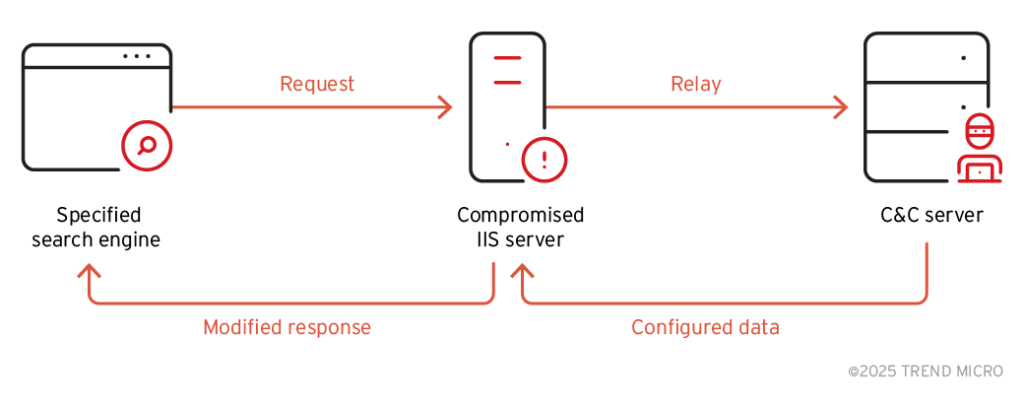
4.Chinese-Speaking Group Manipulates SEO with BadIIS by @TrendMicro
- SEO manipulation campaign that highlights need for orgs using IIS to proactively update and patch systems to prevent exploitation by threat actors that use malware like BadIIS
- campaign is financially motivated since redirecting users to illegal gambling websites shows that attackers deploy BadIIS for profit
- affected countries in Asia such as India, Thailand, and Vietnam. However, its impact can extend beyond geographical boundaries.
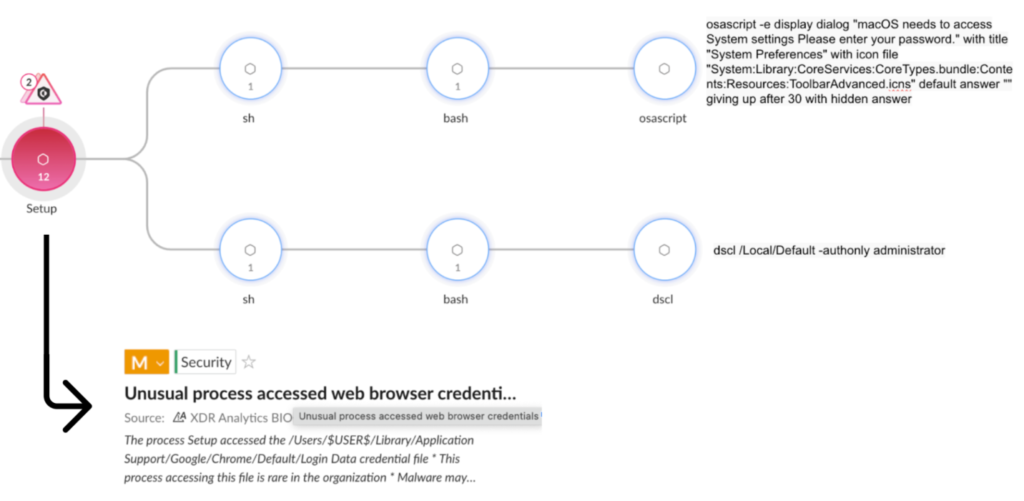
5.Stealers on the Rise: A Closer Look at a Growing macOS Threat by #PaloAlto’s #Unit42
- growing number of attacks targeting macOS users across multiple regions and industries.
- research has identified three particularly prevalent macOS infostealers in the wild: Poseidon, Atomic and Cthulhu
https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/macos-stealers-growing/
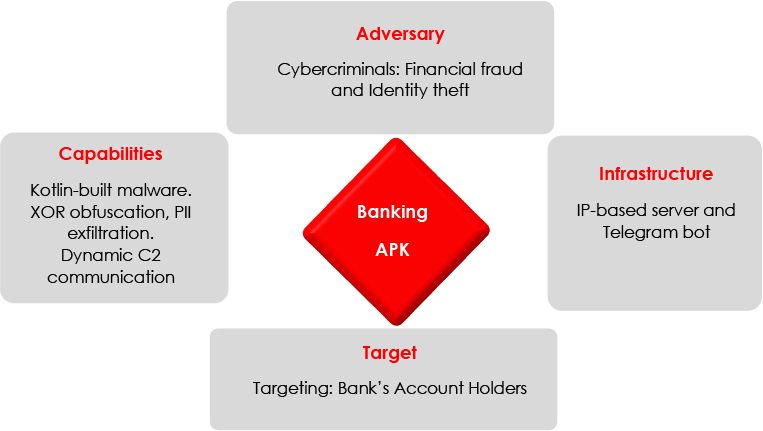
6.FinStealer by @CyfirmaR
- sophisticated malware campaign exploiting a leading Indian bank’s brand through fraudulent mobile applications
- distributed via phishing links, and social engineering, these fake apps closely mimic legitimate Bank apps, tricking users into revealing credentials, financial data, and personal details. The malware employs advanced evasion techniques, including encrypted communication with Command-and-Control (C2) servers, dynamic payload execution, and runtime behaviour alterations, enabling it to bypass detection by security systems.
https://www.cyfirma.com/research/finstealer/
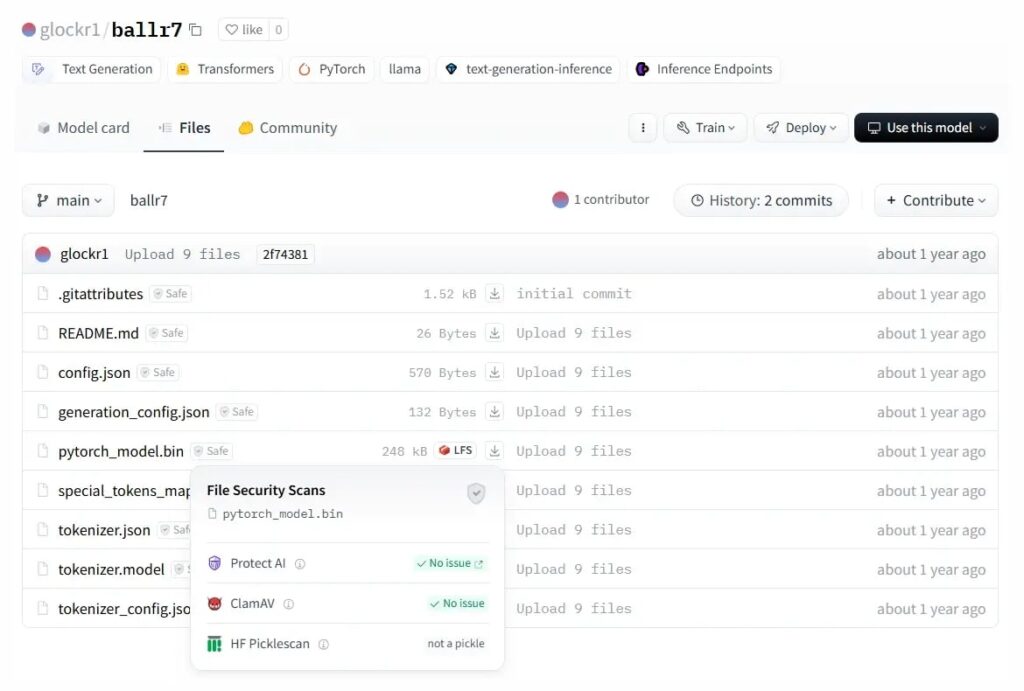
7. Malicious ML models discovered on Hugging Face platform by @ReversingLabs
- research came upon 2 Hugging Face models containing malicious code that were not flagged as “unsafe” by Hugging Face’s security scanning mechanisms
- Pickling packages look like proof-of-concept model for testing a novel attack method
https://www.reversinglabs.com/blog/rl-identifies-malware-ml-model-hosted-on-hugging-face
8. Analyzing ELF/Sshdinjector.A!tr with a Human and Artificial Analyst by #FORTIGUARD LABS
- ELF/Sshdinjector.A!tr – collection of malware that can be injected into SSH daemon
- samples surfaced around mid-Nov 2024
- focus on the reverse engineering of the attack’s binaries and how this reverse engineering was achieved
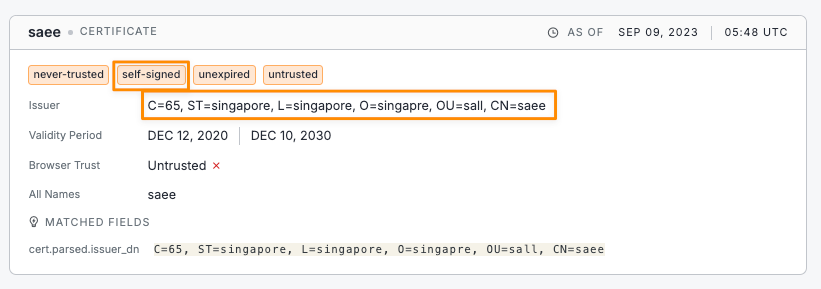
9. Unpacking the BADBOX Botnet with Censys by @censysio
- newly discovered botnet targeting both off-brand and well-known Android devices—often with malware that potentially came pre-installed from factory or further down in supply chain
- 190,000+ infected devices have been observed so far
- suspicious SSL/TLS certificate common to BADBOX infra, revealing 5 IPs and bunch of domains, all using same cert & SSH host key
https://censys.com/unpacking-the-badbox-botnet/
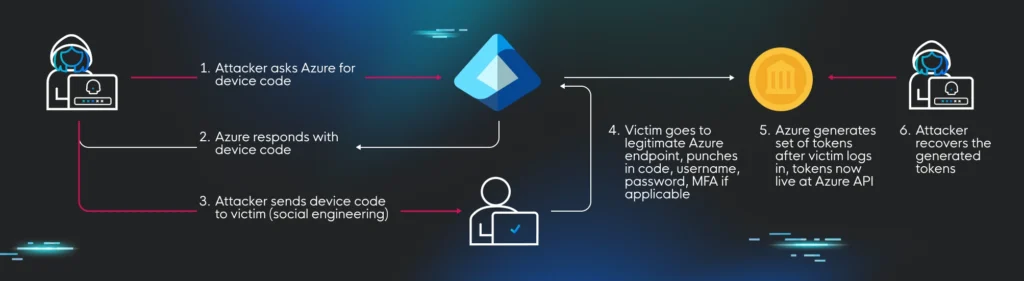
10. Oh, Auth 2.0! Device Code Phishing in Google Cloud and Azure by @HuntressLabs
- Google understands that the device code flow is niche and only used in certain scenarios and limits the scopes available to the device code flow accordingly
- Microsoft makes no such limitations.
https://www.huntress.com/blog/oh-auth-2-0-device-code-phishing-in-google-cloud-and-azure
11. DeepSeek’s Data Breach: Could ProjectDiscovery’s Cloud Have Prevented the Hack? by @pdiscoveryio
- internal ClickHouse instance was left exposed to the internet with no auth, no access controls & no login reqs
- anyone could access database simply by navigating to the /play endpoint on publicly accessible instances
- malicious actor could execute SQL queries and retrieve sensitive data in plain text with ease.
Thank you for reading.
Please add interesting items you came across during the week in the comments below.